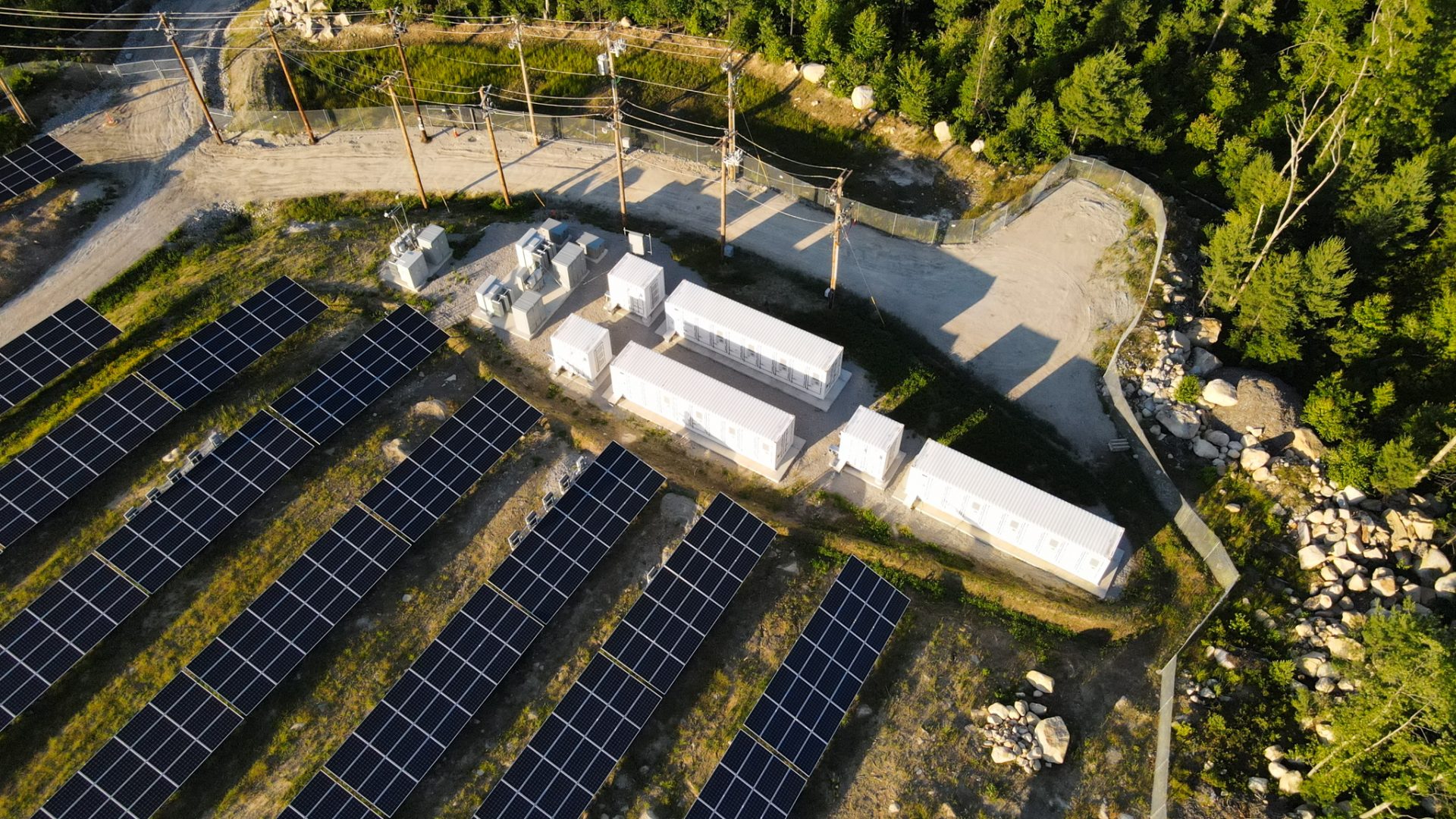
The Intermittency Challenge — and the Battery Energy Storage Systems Solution
As the U.S. energy landscape shifts toward solar, wind, and other renewable resources, one challenge continues to surface across markets: intermittency. While renewable energy is clean, abundant, and increasingly cost-effective, it isn’t always available when the grid needs it most.
Solar production peaks during the day but drops to zero at night. Wind energy can surge or stall depending on the weather. Even hydropower can fluctuate with seasonal water flows. These natural variations create a gap between when energy is produced and when demand is highest — a problem often illustrated by the well-known “duck curve,” which shows steep ramps in energy demand during the early evening hours, just as solar output declines.
This is where Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) are stepping in to help transform the equation.
By storing excess renewable energy during periods of overproduction and releasing it when demand rises, BESS allows clean energy to be dispatched on demand. It effectively decouples production from consumption — giving grid operators the flexibility to smooth out supply fluctuations, reduce curtailment, and avoid relying on fossil fuel peaker plants. In this way, battery storage acts as a bridge between variability and reliability, making intermittent energy sources like solar and wind far more practical at scale. It doesn’t just plug a gap — it enables a more resilient, responsive, and ultimately more sustainable grid.
Current Market Landscape
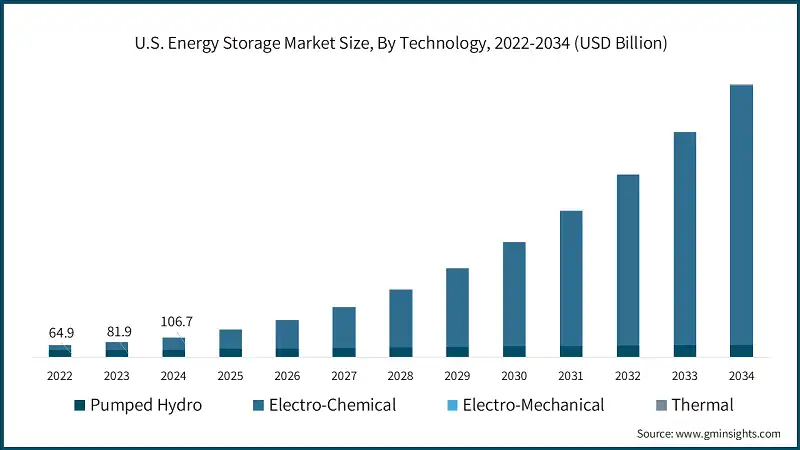
As of 2024, the U.S. energy storage market was valued at approximately $106.7 billion. This robust valuation reflects the nation’s commitment to enhancing grid resilience and accommodating the variable nature of renewable energy sources. The rapid deployment of utility-scale battery storage has been pivotal in this growth trajectory. Notably, in 2024, the U.S. added 10.4 gigawatts (GW) of new battery storage capacity, marking a significant milestone in energy infrastructure development.
Source: Solar Power World | Global Market Insights Inc.
Growth Projections
Looking ahead, the U.S. BESS market is poised for exponential growth. Projections indicate that the market could reach approximately $1.49 trillion by 2034, expanding at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 29.1% from 2025 onwards.
Source: Global Market Insights Inc. | EIA
In terms of capacity additions, 2025 is expected to be a landmark year. Developers plan to introduce 18.2 GW of utility-scale battery storage to the grid, potentially setting a new record for annual capacity growth. This surge aligns with broader trends in utility-scale electric-generating capacity, where solar and battery storage are projected to constitute 81% of the total additions, with solar alone contributing over 50%.
Source: EIA
Technological Advancements
While lithium-ion batteries currently dominate the market, alternative technologies are gaining traction. Sodium-ion batteries, for example, are being explored as a viable option to reduce dependence on lithium supply chains. Companies like Natron Energy have announced plans for substantial sodium-ion battery manufacturing facilities in the U.S., aiming to diversify the energy storage landscape and bolster domestic production capabilities.
Source: Reuters
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the optimistic outlook, the BESS market faces several challenges.
- Supply chain risks: 75%+ of lithium-ion battery production is based in China, raising national security and cost concerns.
- Safety concerns: Incidents like the 2024 battery plant fire in California underscore the need for strict regulation and community engagement.
- Grid integration: Coordinating battery storage with local utilities and transmission infrastructure can still be a complex process.

Conclusion
The U.S. BESS market stands at the cusp of a significant evolution, characterized by rapid growth, technological innovation, and an increasing role in the nation’s energy infrastructure. By helping solve the intermittency problem, BESS enables a clean energy future that’s not just sustainable, but reliable and resilient.
Sources:
- U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA):
https://www.eia.gov/todayinenergy/detail.php?id=64705 - U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA):
https://www.eia.gov/todayinenergy/detail.php?id=64586 - Global Market Insights:
https://www.gminsights.com/industry-analysis/us-energy-storage-market - Reuters:
https://www.reuters.com/business/energy/sodium-ion-set-impact-thriving-us-battery-market-2024-10-03/ - WIRED:
https://www.wired.com/story/us-government-says-relying-on-chinese-lithium-batteries-is-too-risky/ - AP News:
https://apnews.com/article/e5957a710670930ca23c4b2d2e3ed75f